Are egg yolks bad for you?
We all have heard that egg yolk supposedly increases our cholesterol values. But is it true and should we therefore eat egg white only?

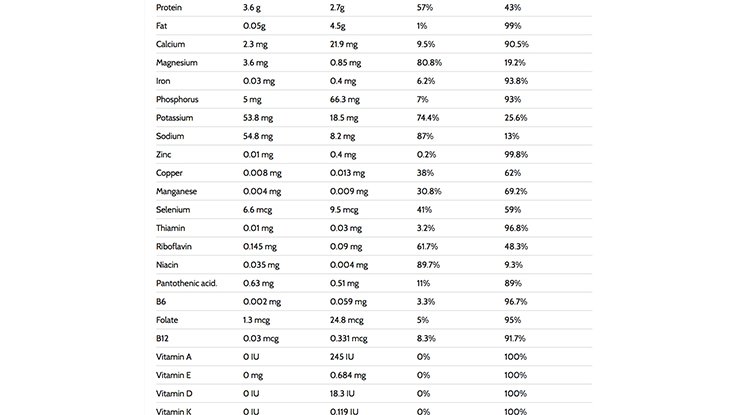
Eggs are a great source of high quality protein: One whole egg contains 5,5 grams of protein in only 68 calories. Egg whites are a low-calorie and fat-free food with 4 grams of protein, 55 mg of sodium and only 17 calories. A single egg white also offers 1,3 mcg of folate, 6,6 mcg of selenium, 2,3 mg of calcium, 5 mg of phosphorus and 53,8 mg of potassium.
It is true that egg yolks carry the cholesterol, the fat and saturated fat of the egg. However, many nutrients such as the fat-soluble vitamins and essential fatty acids come with the yolk. It has around 55 calories, 4,5 grams of total fat of which 1,6 grams are saturated fats. It also contains 210 mg of cholesterol, 8,2 mg of sodium and 2,7 grams of protein.
The table below by the USDA compare the nutrients of the egg white versus the egg yolk. As you can see, 43% of the total protein is in the egg yolk. The egg yolk is a significant source for calcium, iron, phosphorus, zinc, B6 and B12 and folate. The yolk contains 100% of the vitamin A, E, D and K of the egg.
Now should you eat the egg yolk or not? Research suggests that it is saturated fat that raises cholesterol rather than dietary cholesterol. However, if you suffer from coronary artery disease or have any heart health issues like high cholesterol, the recommendation is still to limit your dietary intake of cholesterol and therefore egg yolk consumption. But if you are healthy, one or two egg yolks a day won’t affect your lipid profile. It is perfectly safe and healthy to eat the whole egg in moderation.
When buying eggs, please make sure you get free range eggs from chicken that have been fed organic food. It has been found that eggs sourced from pasture-raised chickens happen to have higher amounts of vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant, as compared to eggs harvested from factory-farmed poultry. What’s more, eggs sourced from factory farms may contain dangerous pathogens like Salmonella. Chickens in concentrated animal feeding operations often live in toxic and polluted environments so it is no surprise these animals, and consequently their eggs too, end up carrying diseases and infections. Antibiotics, hormones and other pharmaceuticals present in factory-farmed eggs are of particular concern as it has been found to cause antibiotics resistance in humans.























